This tutorial describes about the MAC PDU structure when HS-DSCH and E-DCH transport channel are not used. MAC PDUs are also called the MAC Transport Blocks (TB). MAC PDU is a bit string. The MAC PDU is consists of the MAC header and the MAC SDU (RLC PDU) The MAC header size and content depends on the type of logical channel used. The structure of the MAC PDU is as follows. 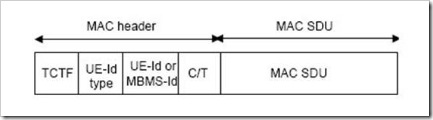
NOTE: The MAC header may have none of the parameters in some cases.
MAC PDU Header Parameters
TCTF: Target Channel Type Field
TCTF field tells the type of logical channel mapped on a Transport Channel. The following combinations can be possible:
Transport Channel: FACH
For FDD Mode:
| TCTF | Designation |
| 00 | BCCH |
| 01000000 | CCCH |
| 01000001-01001111 | Reserved |
| 01010000 | MCCH |
| 01010001-01011110 | Reserved |
| 01011111 | MSCH |
| 0110 | MTCH |
| 0111 | Reserved |
| 10000000 | CTCH |
| 10000001-10111111 | Reserved |
| 11 | DCCH or DTCH over FACH |
For TDD Mode
|
TCTF |
Designation |
|
000 |
BCCH |
|
001 |
CCCH |
|
010 |
CTCH |
|
01100 |
DCCH or DTCH over FACH |
|
01101 |
MCCH |
|
01110 |
MTCH |
|
01111 |
MSCH |
|
100 |
SHCCH |
|
101-111 |
Reserved |
Transport Channel: RACH
Fore FDD Mode
|
TCTF |
Designation |
|
00 |
CCCH |
|
01 |
DCCH or DTCH over RACH |
|
10-11 |
Reserved |
For TDD Mode
|
TCTF |
Designation |
|
00 |
CCCH |
|
0100 |
DCCH or DTCH Over RACH |
|
0101 – 0111 |
Reserved |
|
10 |
SHCCH |
|
11 |
Reserved |
Transport Channel: USCH or DSCH (Only in TDD Mode)
|
TCTF |
Designation |
|
0 |
SHCCH |
|
1 |
DCCH or DTCH over USCH or DSCH |
C/T Field
The C/T field is used to identify the logical channel when multiple logical channels are mapped on the same transport channel. Example: In case of SRB (Signalling Radio Bearer), four SRBs are mapped on the same transport channel. C/T is 4 bit long.
|
C/T field |
Designation |
|
0000 |
Logical channel 1 |
|
0001 |
Logical channel 2 |
|
… |
… |
|
1110 |
Logical channel 15 |
|
1111 |
Reserved |
UE-Id
UE-Id is used to identify a UE on common transport channel. There are mainly two types of identifiers are used:
U-RNTI: UTRAN Radio Network Temporary Identity
U-RNTI is always used in the downlink. The length of the U-RNTI is 32 bits. The U-RNTI is normally associated with connection to a Serving RNC (SRNC).
C-RNTI: Cell Radio Network Temporary Identity
The C-RNTI is used on DCCH or DTCH on uplink and may be used on DCCH on downlink. The length of the C-RNTI is 16 bits. The C-RNTI is normally associated with connection to a controlling RNC (CRNC).
UE-Id Type
The UE-Id type is used to ensure the correct decoding of the UE-Id field in the MAC header.
|
UE-Id Type field 2 bits |
UE-Id Type |
|
00 |
U-RNTI |
|
01 |
C-RNTI |
|
10 |
Reserved |
|
11 |
Reserved |
MBMS-Id
MBMS-Id is used to identify the MTCH for an MBMS service on FACH. MBMS-Id is always used on downlink.
|
MBMS-Id field
|
MBMS logical channel identity [7]
|
|
0000 |
1 |
|
0001 |
2 |
|
… |
… |
|
1110 |
15 |
|
1111 |
Reserved |
Example
In case of Signalling Radio Bearer (SRB), four DCCH logical channels are multiplexed on one DCH transport channel. For SRBs the RLC PDU size is 144 bits.
MAC PDU
|
C/T |
RLC PDU |
C/T field can have the value from 0000 to 0011. 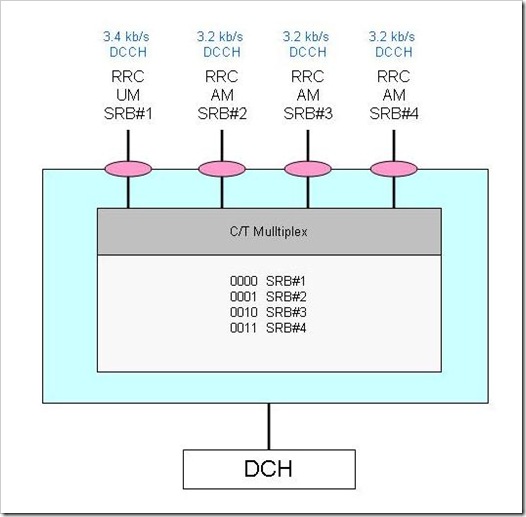
References
Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol specification: 3GPP TS 25.321

Permalink
rq1GEY I want to say – thank you for this!
Permalink
all good things
Permalink
how C/T identify DCCH and DTCH?
Permalink
I have a quick question: When the Node-B forwards a UE’s data packet to the SRNC (i.e., uplink), how does the SRNC know which UE sent this packet?
Thanks a lot in advance,
Jbro