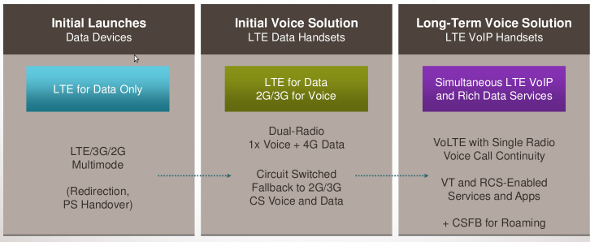
LTE was developed for packet based services. But a majority part of today’s traffic comes from CS based services like Voice and SMS. So 3GPP agreed to provide an intermediate solution for CS (Circuit Swtich) based services till IP based services like VoLTE completely developed and deployed. Using CSFB (CS Fallback) UE can move to GERAN, UTRAN or CDMA2000 systems for voice services. CS fall back services are available in those areas where EUTRA systems overlap with GERAN, UTRAN or CDMA2000.
CS Fallback (CSFB) will be the bridging technology to ensure that LTE smartphone users can enjoy ultra-fast data services as well as high-quality voice services on 2G/3G networks. CSFB will enable devices in packet-switched LTE networks to change over to CS networks for incoming and outgoing voice calls. In many cases, CSFB will co-exist with Voice over Long Term Evolution (VoLTE) well into the future. Going forward, IMS-based Voice over LTE (VoLTE) will be the logical choice to provide voice services over the same technology that is driving the data revolution. There are compelling reasons, however, to provide CS-based voice services for LTE smartphone users, even in markets were LTE networks have been commercially launched. The Next Generation Mobile Networks Alliance (NGMN) has recommended standards-based CSFB to enable non-IMS roaming subscribers to use both LTE data services and voice services in Circuit Switched (CS) networks. With CSFB, when an LTE smartphone makes or receives a voice call, it connects automatically to the 2G/3G network. T he ongoing LTE data session is also transferred to the 2G/3G network. Once the call is terminated, the smartphone reverts to the LTE network. This process is seamless to the end-user.
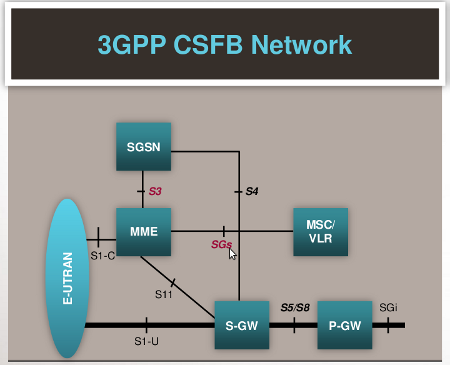
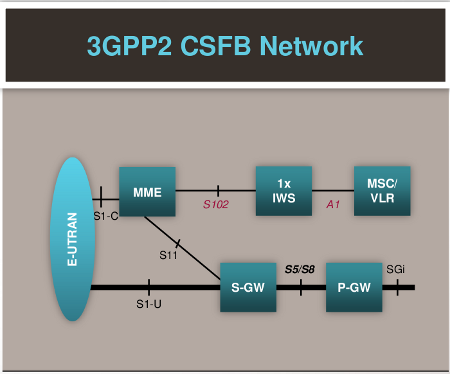
CSFB provides LTE voice capability without requiring significant changes in the existing mobile CS core network, for example in routing or charging configurations. The interface between the CS network and the Evolved Packet Core (EPC), which controls the LTE connection, is the cornerstone of CSFB. The standard SGs interface enables CSFB between these two networks.
LTE Circuit Switched Fallback (CSFB) Architecture
CSFB Performance Summary
Qualcomm had done some performance evaluation of different CS Fallback methods. Here are the results of this.
- Device is registered for both CS and PS services via LTE
- CS voice pages are delivered over LTE
- Device remains on LTE except for voice calls
- SMS can be received over LTE
- For voice calls, UE falls back to UMTS/GSM/C2K
- Mobility methods supported
Different CS Fallback Options
| Method | Target Info | Target Prepared | Measurements | LTE → W | LTE → G | LTE → C2K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Redirection | Target Frequency | No | Optional | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Cell Change Order | Target Cell | No | Required | No | Yes | No |
| Handover-Based | Target Cell | Yes | Required | Yes | Yes | Yes |
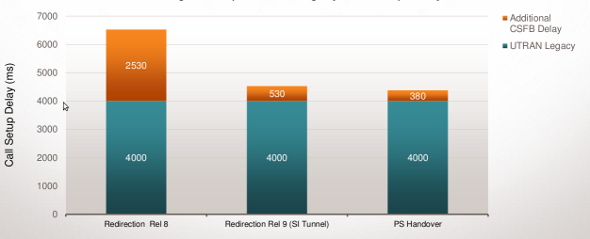
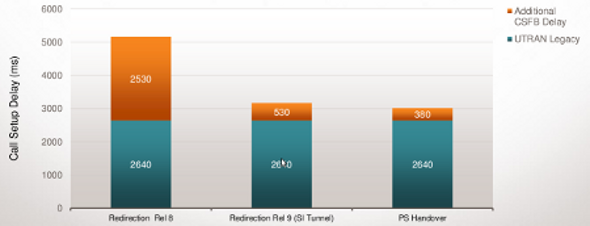
CSFB to UTRAN Call Setup Delay (Mobile-Originated)
Redirection-Based CSFB Call Setup Delay with SI Tunneling Is Comparable to Legacy Call Setup Delay
CSFB to UTRAN Call Setup Delay (Mobile-Terminated)
Redirection-Based CSFB Call Setup Delay with SI Tunneling Is Comparable to Legacy Call Setup Delay
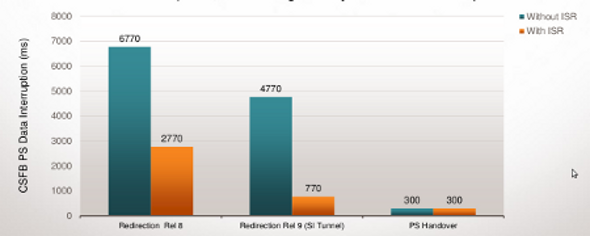
CSFB PS Data Interruption
The Handover Option Provides the Lowest Data Interruption Time; For the Redirection Options, ISR Can Significantly Reduce Data Interruption Time
CSFB to GERAN Call Setup Delay (Mobile-Originated)
RRC Release with SI Tunneling Provides the Best CSFB Solution

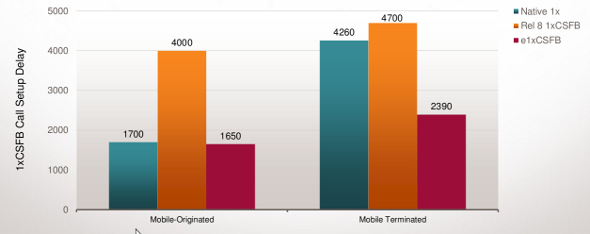
1xCSFB Call Setup Delay
e1xCSFB Offers the Shortest Call Setup Time
Conclusion
- CSFB offers a solution with the cost, size, and battery life advantages of single-radio solutions, LTE data speeds, and reliability/ubiquity of 2G/3G voice
- Redirection-based CSFB using Release 9 SI Tunneling, for both 3G and 2G offer call delays within subseconds of legacy call setup delay
- Redirection-based CSFB offers call reliability on par with legacy call setup reliability Compared to dual radio solution, e1xCSFB offers more cost effective device solution and also with shorter call setup delay

Permalink